Final week, the Plane Accident Investigation Fee, shaped by the Authorities of Nepal to analyze the accident of 9N-AME on the twenty fourth of July 2024, launched their last report. There’s rather a lot occurring right here, so I hope you’re seated comfortably!
New! You too can take heed to an robotically generated audio file of the article!
It ought to have been a easy ferry flight, below 150 kilometres. The proprietor and operator, Saurya Airways, is a Nepalese home provider based in 2014 with a single Bombardier CRJ 200. In 2017, they bought a second CRJ 200, registered in Nepal as 9N-AME, as a back-up plane. As of July 2024, this was their solely operational plane.
Besides that it wasn’t operational. That CRJ 200LR had been grounded for 34 days .
The day earlier than the accident, the Air Transport Division of the Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal authorized the ferry flight for the plane to fly from Tribhuvan Worldwide Airport in Kathmandu to Pokhara Worldwide Airport, the place the CRJ 200LR was to bear base upkeep (C-check). The plane had already undergone preservation of plane and return to service upkeep checks.
That morning, the primary officer was first to reach within the cockpit, whereas Saurya Airways personnel loaded the cargo. The bottom employees stated the cargo part was fully full, in order that they needed to load the remaining baggage and tools into the cabin.
Saurya Airways was the primary officer’s first employer; he had been with the airline since he’d completed his industrial coaching in 2021. When changing the CRJ 200, he’d failed his preliminary simulator test, which led to him extending his coaching in Germany by three months. This considerably elevated his coaching prices, which was added to his bond with Saurya Airways, that means he needed to stay with the airline or else pay again the remaining stability. On prime of this, he had needed to take out a mortgage to fund his dwelling prices in Germany for the extra coaching.
He’d then been laid off by the airline for an unspecified time however later reinstated “primarily based on flight hours”. His obligation and flight hours have been considerably decreased, as the corporate’s operations have been low. His simulator efficiency was marked as Passable.
Whereas the primary officer went via the pre-start checks, the flight dispatcher known as with the plane weight and stability: 18,137 kilogrammes.
The primary officer would use the plane weight, together with the environmental circumstances and the runway parameters, to find out the V-speeds for the flight and enter them into the flight administration system.
The important thing take-off speeds are V1, which is the pace at which a take-off ought to now not be aborted, VR, the pace at which to rotate the plane, lifting the nostril for take off, and V2, the pace at which the plane can nonetheless safely climb with one engine out. These speeds are calculated earlier than each flight, marked on the airspeed with colored bugs, and repeated as a part of the pre-flight briefing.
Now that the primary officer had the take-off weight of the plane, he might use the speedcard booklet to calculate the V-speeds for the flight.
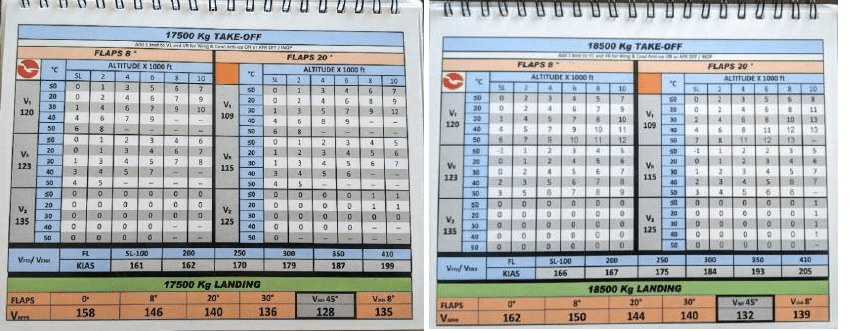
He flipped to the cardboard for 18,500 kg take-off weight and used the bottom V-speeds for flaps at 20° (V1: 109, VR: 115) V2: 125) to calculate the right speeds for the CRJ 200 primarily based on their altitude of 4,400 ft above sea degree.
V1 (take-off choice pace): 114 knots
VR (rotation pace): 118 knots
V2 (take-off security pace): 126 knots
The captain arrived on the cockpit. He had joined Saurya as a primary officer in 2015 and was promoted to captain in 2017. Now he served each as a captain and as Saurya’s Operations Director. His simulator efficiency was marked as Glorious.
There have been half-hour till the supposed take-off. The captain requested in regards to the checks that the primary officer had completed to this point and offered supervisory directions. A 3rd crew member, an Plane Upkeep Technician, joined the flight crew they usually mentioned the C-Examine deliberate in Pokhara and “different informal matters unrelated to the flight” with a number of the employees within the cabin.
At that time, the flight crew have been contacted to say that they wanted to delay their departure, as extra personnel have been anticipated. The captain responded a minute later that they have been going to need to cancel engine start-up. Air Visitors Management observed the identical factor, calling the crew to ask whether or not they wanted their taxi to be delayed. The crew responded that they wanted extra time, as much as 30 extra minutes.
The remaining Saurya personnel arrived at that time and the cabin door was closed. The crew initiated begin up of each engines they usually started to taxi, doing the management floor checks alongside the best way. The flaps have been prolonged to twenty°. They entered runway 02 and carried out a backtrack to the edge with the intention to use the total size of the runway.
At precisely 11:10 native time, the crew known as from runway 02 that they have been prepared for departure.
At 11:10:25 they utilized energy for take off with each engines N1 energy reaching 92% inside 13 seconds. They skipped the remainder of the pre-take-off guidelines and started accelerating down the runway.
The primary officer known as out V1. A second later, the captain abruptly pulled again on the yoke. This abrupt elevator enter, going from 1.5° to 10° elevator deflection over one second, prompted a fast pitch up that peaked at a staggering 8.6° per second, versus the anticipated 3° per second pitch up.
The plane lifted sharply into the air, travelling just below 120 knots computed airspeed, simply above the computed VR (rotation pace). The primary officer will be heard on the Cockpit Voice Recorder saying “Woah….woah…woah”.
The plane was travelling at 131 knots as they climbed to 11 ft above the runway. The stick shaker activated, warning of an impending stall.
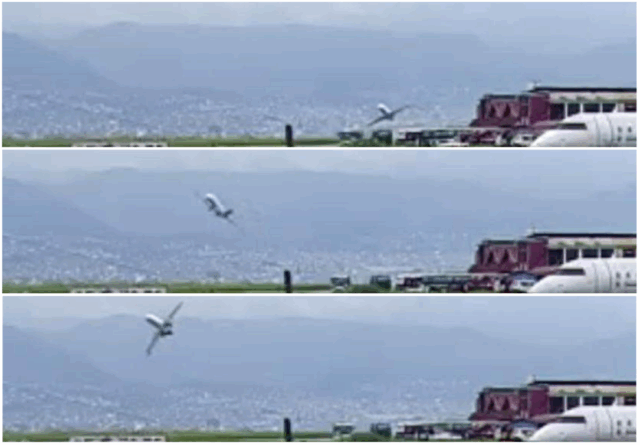

From the surface, bystanders noticed the CRJ 200 rolling to the best, then banking sharply and rolling to the left, solely to roll again laborious to the best. The plane was practically inverted as they continued rolling proper, climbing via 77 ft.
The timing on this isn’t precise however the first officer was nonetheless talking, calling out “Sir, sir, sir!”
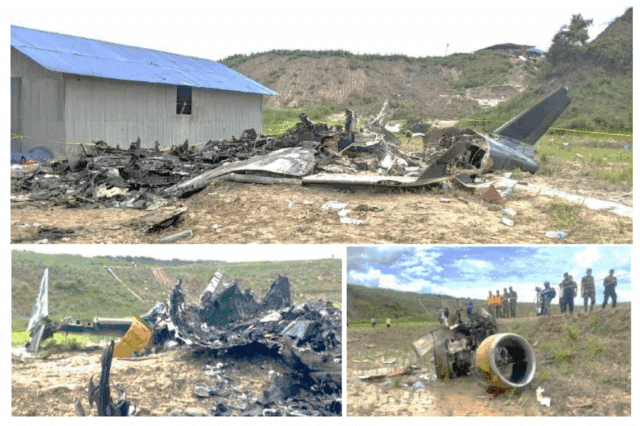
The proper wing smashed into the runway, simply earlier than the intersection of taxiway Juliet. The CRJ 200 cartwheeled onto the east aspect of the runway and continued east, placing a cargo container and shed belonging to Air Dynasty Heli Providers earlier than bursting into flames.
The plane had taken off at 11:10:55. Through the oscillations, the plane reached a peak of simply over 100 ft above the runway. The FDR stopped recording 13 seconds after take off, at 11:11:08.
4 fireplace autos have been dispatched the second the best wing struck the bottom. The plane had fallen right into a gorge, sliding down 130 ft over the subsequent 4 seconds. The hearth autos struggled to succeed in the crash website. The primary fireplace car discovered a place and started spraying water whereas the subsequent two autos paused, not instantly participating within the fire-fighting efforts. Rescue personnel helped the captain who escaped from the cockpit embedded within the cargo container however no effort was made to rescue the remaining crew from the cockpit earlier than it burst into flames.
The entrance of the passenger cabin was instantly totally engulfed in fierce flames, with no risk of rescuing anybody from the entrance.
Along with the flight crew, there have been sixteen folks seated within the passenger cabin, together with a four-year-old little one. Of the 19 on board, fifteen have been killed within the affect. Three have been pulled from the wreckage of the cabin; nonetheless they died en path to the hospital. The captain, who suffered critical accidents, was the one survivor.

4 months earlier than the accident, the plane underwent an inspection for the renewal of the Certificates of Airworthiness. The report doesn’t specify the outcomes of this inspection apart from that the MLG TBO (Most important Touchdown Gear Time Between Overhaul) was set to run out in April. The airline obtained an extension to do that upkeep, giving them till June to finish the work wanted. In April, Saurya additionally obtained a particular allow for a take a look at flight to resume the now-expired Certificates of Airworthiness.
However they didn’t get the upkeep completed in time. On the nineteenth of June, a month earlier than the accident flight, the extension for the touchdown gear upkeep expired. The plane registered as 9N-AME was grounded.
The operator was clearly struggling to get the CRJ 200 again into service. The truth that they wanted extensions and particular permits to take care of the continued certification points means that the airline was struggling to keep up their fleet correctly, although the fleet consisted of just one plane at this level.
Saurya repeatedly organized for short-term storage for the plane till the twenty second of July, two days earlier than the accident, when each principal touchdown gear assemblies have been lastly eliminated and reinstalled as per the mandatory overhaul.
The next day, the Air Transport Division of the Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal authorized a one-time non-revenue ferry flight for 9N-AME to fly to Pokhara Worldwide Airport, the place it could bear base upkeep (C-check).
The query stays: why have been there 19 souls, together with a younger little one, on board an plane flying for upkeep on a particular ferry flight allow?
That morning, the day of the accident, the plane underwent a return to service test.
It’s essential to notice that the investigation discovered no mechanical defects that contributed to the accident. The upkeep work was accomplished correctly, and flight information confirmed all plane methods functioned usually in the course of the take-off sequence.
The loading of the plane, however, was trigger for critical concern. The load sheet estimated 600 kg of luggage however they solely discovered 402.5 kg on the crash website. Then they discovered an extra 98.6 kg had been faraway from the crash website with out being processed. This baggage was recovered from Saurya company places of work in what the investigators later known as out as proof tampering.
Notably, this nonetheless leaves the plane 100 kilograms wanting the acknowledged load for the flight.
The bottom crew stated that the maintain was full and extra cargo needed to be loaded into the plane cabin. This was completed in a haphazard method, with lubricants, contact cleaners, wheel chocks, toolboxes and meals gadgets merely dumped onto seats and within the aisles with out being secured. Among the many wreckage, investigators discovered hydraulic fluid spilt on the ground of the cabin and proof of harmful items, together with flammable contact cleaner (categorised as UN1950 hazardous materials), loaded with out correct documentation or securing. Saurya Airways didn’t have a allow for transporting harmful items.
The captain and the flight dispatcher have been conscious that this baggage had been loaded into the passenger cabin however didn’t see it as a degree of concern.
Apparently, this was enterprise as regular.

The crash was made worse by the truth that Tribhuvan Worldwide Airport’s runway security areas didn’t meet worldwide requirements established by ICAO Annex 14. The investigation discovered that the low-lying areas on the east aspect of the runway, the place 9N-AME crashed, didn’t adjust to necessities for runway strips.
Runway strips function security zones for plane that overshoot, overrun, or veer off runways throughout takeoff or touchdown accidents. They should be freed from obstacles and maintained to permit fast entry for rescue and firefighting autos. At Tribhuvan, the non-compliant areas surrounding the runway had been flagged for over a decade with out significant correction. If the runway strip had met ICAO requirements, the crash would have taken place throughout the security space. As a substitute, the wreckage was in tough and uneven terrain, creating confusion for rescue crews and delaying their response.
The crash space had by no means been included in emergency workout routines, so the firefighting and rescue crews had no plan for accessing that terrain. Solely the lead unit engaged in energetic firefighting. The opposite three autos arrived however stopped wanting the wreckage, unsure about entry and unclear on their orders. They’d entry to foam tenders and dry chemical brokers however used solely fundamental water spraying.
To make issues worse, the emergency gate nearest to the crash website was closed, blocked by development supplies and different particles.

The end result was a disjointed and incompetent emergency response when each second was important. The investigation concluded that with correct rescue coordination and compliant runway security areas, the primary officer and upkeep technician within the indifferent cockpit could have survived, as an alternative of being swallowed by flames whereas rescuers made no co-ordinated effort to rescue them.
There was no cabin crew on board, regardless of the presence of 16 passengers, together with a toddler. No security briefing was made, nor was anybody on board to make sure that fundamental security measures have been compliedwith. A lot of the occupants of the passenger cabin have been killed by blunt pressure accidents. The rescue and fireplace combating groups didn’t doc whether or not the passengers have been carrying seatbelts, which leavesus with little to go on as to the damage patterns.
All this, on what was meant to be a particular approval ferry flight. Nepal has a number of laws concerning ferry flights, referencing the EU steerage that ferry flights are for non-airworthy civil plane. Nonetheless, the CAAN paperwork will not be fully clear, defining ferry flights as Particular VFR flights with no passengers carried in a single doc and that individuals on board shall be restricted to “flight crew and upkeep folks” in one other doc, FOR(A) Nepal Para 8.7.4.
The Saurya employees weren’t important to the flight, however strictly talking, the vast majority of them have been upkeep folks, which might arguably be justified primarily based on paragraph 8.7.4. Even when we settle for that, nonetheless, it doesn’t clarify why relations have been on board, together with a small little one, the improperly loaded cargo or why the flight was operated with out cabin crew.
We can’t get the solutions to those questions. These killed within the crash included Saurya’s Supervisor of Persevering with Airworthiness Administration Organisation, which is deeply ironic below the circumstances, but in addition signifies that the investigation couldn’t decide the justification for loading the plane with non-essential personnel. Additionally killed have been the Upkeep Supervisor, the Airline Security Supervisor and QA supervisor.
It’s troublesome to think about that they didn’t suppose to touch upon the hazardous flammable items merely tossed into the cabin.
As a result of there have been no formal check-in procedures for these boarding the airplane, the cargo and private gadgets weren’t weighed. The bottom crew (bizarrely, talked about because the advertising and marketing division within the report) got a crude estimation of the luggage weight, which they wrote down for the loading manifest. The cockpit voice recorder features a dialog between floor and upkeep personnel discussing the tough weight estimation, which the flight dispatcher then listed as 18,137 kg on the load and trim sheet.
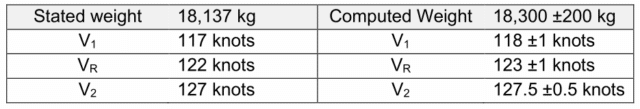
The investigators tried to reverse-engineer the precise plane weight utilizing physics and flight information. Remarkably, the precise weight was not far off, round 18,300, plus or minus 200 kilos.
Based mostly on this, the V-speeds ought to have been calculated at V1=118, VR=123, V₂=127.5 knots.
However we all know that the crew truly rotated at below 120 knots, nearer to V1 than VR. Positive, the plane was heavier than estimated; nonetheless that ought to solely have led to a discrepancy of 1 knot for V1 and VR and solely half a knot for V2.
The issue, it seems, was the speedcard.

Bear in mind these base speeds for 18,500 kg take-off weight?
Sadly, these numbers have been flawed. In truth, the V-speed references on that web page have been a direct copy of the right V-speeds for a take-off weight of 17,500 kg.
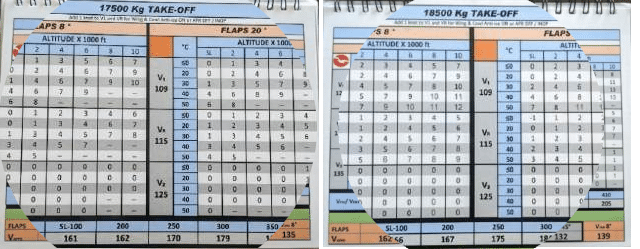
The bottom crew had estimated the load of the plane to inside a couple of hundred kilos. However the speedcard within the plane was 1,000 kilos out.
From the report:
The truth that not one of the flight crew observed the blunder within the speedcard though-out the historical past of the airline is a important failure of the flight operations and security administration.
The speedcard had been flawed for ten years. Nobody at Saurya Airways had ever observed.
The captain, the one survivor of the flight, recalled that he had not confirmed the V-speeds calculated by the primary officer, which he ought to have completed as normal. However he was additionally not conscious of the error within the speedcard and so wouldn’t have questioned the V-speeds, which the primary officer had calculated appropriately primarily based on the speedcard information.
Now we see the true concern: a rotation pace of 118 knots as an alternative of the required 123 knots.
The stall pace of the CRJ 200 was 111 knots. The captain, as Pilot Flying, rotated at just below 120 knots, solely 9 knots above the stall pace. He shortly deflected the elevator from 1.5° to 10° over only one second, thrice sooner than normal rotation, pitching up abruptly as if attempting to unstick the plane by brute pressure.
Each wings reached a dangerously excessive angle of assault, inflicting the stick-shaker to activate to warn the pilots that the plane was liable to stalling. Based mostly on historic information, the plane’s proper wing was liable to stalling first, true for each of the airline’s CRJ 200s, truly, and that’s what occurred right here.
The CRJ 200 suffered an uneven stall as the best wing misplaced carry. The plane started to roll to the best with a financial institution angle of 26°. The captain reacted because the stick shaker activated, rolling left and holding it for 2 seconds. The plane rolled left 55° at 50 ft above the bottom. The plane lurched as much as 100 ft earlier than pitching again down. They rolled laborious to the best to 94.6° (practically inverted). There was no likelihood of restoration.
The primary officer tried to intervene however was unable to speak successfully, repeating “woah” and “sir” as an alternative of one thing helpful like “scale back pitch!”
The flawed V-speeds arrange the damaging circumstances. Nonetheless, it was that preliminary extreme pitch up by the captain that began them on the trail to lack of management. A traditional rotation must be most 3° per second. There’s a warning within the CRJ 200 handbook that the kind is inclined to regulate points on take-off with extreme pitch charges/overrotation. The Saurya Airways take-off procedures, nonetheless, didn’t point out the significance of a 3° per second rotation charge.
In truth, excessive rotation charges of over 4° per second have been frequent at Saurya. The plane’s flight information recorder confirmed 18 situations of excessively excessive pitch charges above 5°/second over the earlier yr. Probably the most excessive circumstances have been a take off at 5.8°/second in January 2024 and 5.5°/second in March 2024. That March 2024 flight was the captain, the identical who would turn out to be the only real survivor of the accident flight.
The accident flight’s 6.5°/second was the very best ever recorded. Nonetheless, this wasn’t only a easy pilot error on a single flight; it was the airline tradition. Nobody at Saurya Airways was monitoring or correcting this harmful approach.
About these rotations… We’re fortunate to have that historic information as a result of the investigation additionally discovered that the Flight Knowledge Recorder had been malfunctioning since at the very least 2021 with out anybody noticing. It was the duty of CAAN (Nepal’s civil aviation authority) to confirm the FDRs to verify that each one necessary parameters are being recorded. Yearly. They didn’t discover something flawed for at the very least 4 years.
Key lacking parameters included Management column forces (how laborious pilots pushed/pulled), Management wheel forces (roll inputs), Rudder pedal forces and positions and brake pedal functions. With out the management pressure information, investigators can’t recreate how aggressively the captain pulled on the controls or whether or not the primary officer tried to bodily intervene.
The shortage of oversight by the regulator was not a one-off concern. A security audit in September 2023 discovered that CAAN had insufficient coaching for its inspectors. The audit recognized systemic weaknesses within the CAAN security programmes and the frameworks for monitoring security methods. Moreover, CAAN was fighting useful resource shortages and personnel administration points, which instantly affected its means to supervise airline operations.
I do know this has been a really lengthy article however, really, this accident is difficult to imagine, not to mention clarify. Each degree of the aviation security system failed concurrently: crew procedures, airline operations, plane efficiency information, regulatory oversight, airport emergency response, and even post-accident proof dealing with.
The ultimate report lays the blame firmly at Saurya’s failures.
Most Possible CauseThe most possible reason behind the accident was a deep stall throughout take-off due to an abnormally fast pitch charge commanded at a decrease than optimum rotation pace.
Contributing Elements
The contributory components to the accident are:
Incorrect speeds calculated primarily based on faulty speedcard. The interpolated speedcard of the operator for 18,500 kg TOW mentions incorrect V-speeds for take-off. This error within the speedcard went unnoticed since its growth. There was no acceptance/approval of the speedcard booklet.
Failure to determine and deal with a number of earlier occasions of excessive pitch charge throughout take-off by the operator.
The operator confirmed gross negligence in complying with the prevailing practices of ferry flight planning, preparation and execution. There’s a lack of constant definition of ferry flights.
Gross negligence and non-compliances by the operator throughout the whole means of cargo and baggage dealing with (weighing, loading, distribution and latching), whereas violating the provisions of operational handbook and floor dealing with handbook. The load was not adequately secured with straps, tie-downs, or nets, whereas the flight preparation was rushed.
The report concludes with a set of instant actions and longer-term systemic adjustments. Saurya Airways has since revised and verified their pace playing cards and applied stricter take-off procedures, with focused retraining for pilots on stall recognition, pitch management and plane efficiency monitoring. They’ve additionally launched a Flight Knowledge Monitoring system to detect unsafe traits. Cargo dealing with procedures have been overhauled.
Emergency response protocols at Tribhuvan Worldwide Airport have been up to date, and stricter evidence-handling procedures have been mandated after post-crash investigation points.
The Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal says that they’ve tightened their oversight with elevated ramp inspections, common operational audits, and new guidelines for plane loading and documentation.
I want Nepal’s aviation business all one of the best, but it surely’s laborious to really feel assured about their success given the atmosphere that allowed such a breakdown to happen within the first place.
Individuals typically ask me what airways I’d keep away from flying with. My reply is that it’s not any particular person airline that causes me concern a lot because the regulator. When the system is damaged on the prime, the failures filter down.
Nepal’s Civil Aviation Authority must do much more to earn my belief within the airways they declare authority over.





