Investigators say a hydraulic becoming failure set off the 2022 B-2 incident at Whiteman AFB, ending in a gear collapse, wing fireplace and $300M restore invoice.
The U.S. Air Drive has launched the Accident Investigation Board (AIB) report into the B-2A Spirit mishap at Whiteman AFB on Dec. 10, 2022, offering an in depth, technical reconstruction of occasions from method to firefighting. The findings level to a hydraulic becoming failure that triggered a cascade ending with a main-gear collapse on touchdown, a wing fireplace and important injury to the plane. No accidents have been reported.
Occasions
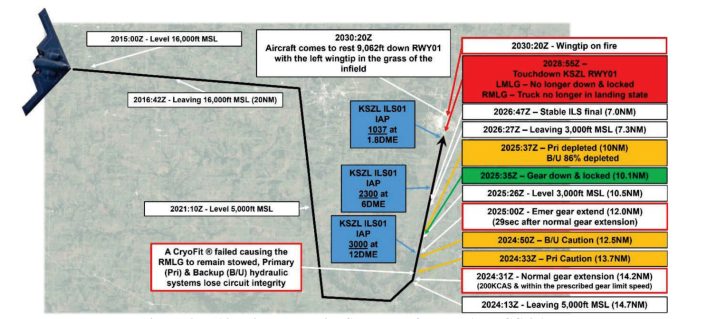
In keeping with the AIB, tail quantity 90-0041, callsign DEATH 12, launched at about 0700 native because the airborne spare for a long-range mission and returned to Whiteman as soon as the first plane continued, as deliberate. The method to Runway 01 was uneventful till the crew chosen gear down at roughly 200 KCAS (inside limits). Instantly afterward, the plane offered a grasp warning and hydraulic system cautions indicating a leak. The left foremost and nostril gear prolonged; the precise foremost gear didn’t. The crew executed the emergency extension, after which all three gear indicated down and locked, and the plane was cleared to land.
Landing occurred close to the 1,000-ft markers at about 1429 native. On contact, the left foremost touchdown gear (LMLG) collapsed. The left wing then contacted the floor and the plane departed the paved floor earlier than coming to a cease with the left wing within the grass infield. The crew egressed with out damage. The AIB notes the engineering parameters at touchdown (pace, perspective and recorded masses) didn’t point out a tough touchdown, focusing consideration as an alternative on the landing-gear system habits following the prior emergency extension.
The report attributes the initiating occasion to the expulsion of a hydraulic coupling related to the precise foremost gear truck place sequence valve. The expelled sleeve opened a path for hydraulic fluid to be pumped overboard, first from the first hydraulic system after which from the backup system because the flight-control computer systems switched sources in response to falling stress. The leak prevented the precise foremost gear from unlocking within the regular sequence and drove the crew to make use of the emergency extension. Observe-on supplies evaluation discovered circumferential “witness marks” on the T-fitting in step with a single expulsion occasion; no microcracking or floor flaws have been recognized within the recovered coupling itself.
Why the left foremost failed after an apparently profitable extension
The AIB’s technical evaluation focuses on what occurred contained in the landing-gear hydraulics throughout emergency extension. When the system shifted to the emergency bypass configuration, the stress that usually helps maintain the left foremost’s lock hyperlink in an over-center (locked) place quickly dropped. That change allowed the lock actuator to loosen up barely earlier than touchdown. On landing, a quick stress pulse related to truck-beam motion and the truck-position actuator return move pulled the lock hyperlink additional out of over-center, overcoming spring pressure and resulting in the LMLG collapse. In brief: the emergency extension resolved indications, however the left foremost not had the hydraulic margin it usually retains by way of touchdown.
Because the wing dragged, the underside pores and skin abraded throughout unprepared floor and concrete, rupturing the left surge tank underneath the wingtip. A gasoline fireplace began and later concerned the left outboard tank. Plane rescue and firefighting (ARFF) items responded promptly. The incident commander initially directed water software; Aqueous Movie Forming Foam (AFFF) was approved roughly three minutes and 28 seconds after the beginning of the assault, as soon as the hearth was assessed as fuel-related. Exterior flames have been considerably diminished with foam, however warmth throughout the wing continued to construct. The left surge tank then exploded, adopted by the left outboard tank roughly ten minutes later. The second explosion blew a bit of higher wing pores and skin free, after which firefighters have been capable of entry and extinguish the inner fireplace; the hearth was out roughly one hour after it started. No responders have been injured.
Injury and price
The left wing sustained main structural injury, together with injury to manage surfaces and the left main-gear doorways and actuators. The AIB’s estimate locations plane injury above $300 million; airfield injury was roughly $27,500.


The AIB president finds, by a preponderance of proof, that the mishap was brought on by the failure of the truck place sequence valve’s CryoFit coupling, which led to hydraulic loss, an emergency extension, and subsequent situations that allowed the left foremost to break down on landing. Two considerably contributing components are cited:
landing-gear design vulnerabilities that permitted the left foremost lock hyperlink to maneuver out of its required over-center place throughout emergency configuration, leaving it vulnerable to break down; and
a delay in using AFFF, which allowed the hearth to unfold and elevated exterior injury. The board notes there have been no recognized deviations from directives or coverage by aircrew or maintainers that contributed to the mishap.
The report additionally explains that speedy use of froth would have diminished exterior injury however wouldn’t have modified the end result contained in the sealed tanks; the inner fireplace was liable for the explosions that occurred regardless of the exterior assault. The board additional data that one ARFF car with a piercing nozzle was unavailable on account of a upkeep difficulty and one other suffered a pump failure in the course of the response. Technical steering for B-2 wing/fuel-tank piercing is proscribed, which left uncertainty over how a penetrating nozzle may need been employed even when accessible.
The AIB report focuses on the technical chain of occasions, injury evaluation and firefighting response however it doesn’t doc the bottom’s operational standing after the mishap (runway closure period, reopening timeline, or the following fleet stand-down).
Nevertheless, as we lined in particulars, within the speedy aftermath, Whiteman AFB’s solely runway was closed, initially through NOTAM by way of Dec. 16, later prolonged to Dec. 31, 2022, whereas Air Drive International Strike Command ordered a security stand-down of your complete B-2 fleet.
A couple of days later, the bottom introduced that the runway had reopened on Dec. 21, 2022, permitting A-10 and T-38 flying to renew, whereas the B-2s remained grounded pending inspections. Subsequent stories highlighted the runway had been closed 11 days in complete and that B-2 flight operations resumed on Might 22, 2023, after roughly 5 months of stand-down.
CryoFit fittings and upkeep
CryoFit sleeve couplings are used extensively within the B-2’s titanium hydraulic plumbing. Put in chilly and shrunk into place, they create a mechanical chunk into the adjoining tube or becoming. The AIB describes the set up technique and notes that, on this case, laboratory inspection didn’t establish materials defects within the expelled sleeve; witness marks urged a single-event expulsion. The report doesn’t attribute the mishap to upkeep error; preflight servicing and inspections complied with technical orders, and the plane launched with out discrepancies.
Procedural takeaways
In keeping with the report, system indications might be needed however inadequate: all three gear confirmed down-and-locked after emergency extension, however the left foremost not retained its full locking margin, info indirectly captured by cockpit standing. Second, firefighting agent choice issues on gasoline fires. The AIB underscores that Air Drive coverage didn’t prohibit AFFF’s early use; the incident commander’s preliminary hesitation was based mostly on an interpretation later recognized as an “unwritten coverage” difficulty.
Summing up…
The Whiteman mishap was initiated by a hydraulic coupling failure and compounded by the way in which the landing-gear system behaves when shifted to emergency hydraulics. The next fireplace injury displays each the mechanical injury from the gear collapse and the timeline of firefighting actions. The AIB’s suggestions deal with engineering evaluation of the landing-gear hydraulics in emergency mode, evaluate of fittings, and readability in ARFF coaching for agent choice and entry on low-observable airframes.
Readers might recall a earlier Whiteman incident on Sept. 14, 2021, when B-2A 89-0129 “Spirit of Georgia,” assigned to the 393rd Bomb Squadron, suffered a left foremost touchdown gear collapse on landing and skidded off the runway. We reported the AIB’s discovering that previous/weak lock-link springs on the left foremost have been the first trigger, with injury estimated at about $10 million; each pilots have been unhurt. The jet got here to relaxation off the pavement roughly a mile from the landing level, prompting a runway closure whereas restoration operations befell.





