On September 30, 2017, an Air France Airbus A380 working flight AF066 from Paris Charles de Gaulle to Los Angeles suffered an uncontained engine failure whereas cruising over southern Greenland.
After the failure, the plane’s heading elevated by three levels to the correct in three seconds, and there have been vibrations within the airframe for round 4 seconds. Nevertheless, regardless of the engine failure, the flight crew maintained full management of the plane and made a secure emergency touchdown at a distant Canadian airport.
Flight Particulars
The Airbus A380-800 with registration F-HPJE was performing flight AF066 from Paris CDG to Los Angeles (LAX) with 497 passengers and 24 crew members. The captain in command had logged greater than 19,000 flight hours, together with 3,249 hours within the A380. Through the take-off, the primary officer was the pilot flying (PF) and the captain was PM.
Departing Paris Charles de Gaulle at 09:50 native time, the flight proceeded uneventfully for a few hours. The crew adjusted the cruising ranges a number of occasions in the course of the transatlantic crossing, finally stabilizing at FL370 by 11:14 UTC.
Subsequently, at 13:48 UTC, whereas flying over the distant icy terrain about 100 nautical miles southeast of Greenland, the crew requested to climb to FL380. Clearance was granted, and the engines started spooling up — their low-pressure compressor and turbine rotation speeds (N1) rising from 98% to 107%, near the redline restrict.
One minute later, Catastrophe Struck!
Roughly 5 hours into the flight, whereas cruising at 37,000 toes, the plane’s quantity 4 engine (the rightmost engine) stalled, ejecting its entrance fan and cowling midair. The titanium fan hub fractured into a minimum of three items resulting from a beforehand undetected chilly dwell fatigue crack, ejecting large fragments from the engine.
Two main elements have been launched violently, one upward, one downward, destroying the ahead cowling and separating all the air inlet, which fell onto Greenland’s ice sheet. Though particles hit the wing and fuselage, vital methods remained intact.
The plane shuddered violently. The crew heard a loud bang, the flight path skewed barely to the correct, and the airframe shook for about 4 seconds. The Digital Centralized Plane Monitoring (ECAM) system displayed an “ENG 4 STALL” warning.
Following the engine failure, the captain took handbook management, engaged autopilot 1 briefly, and ordered the ECAM engine shutdown guidelines. Engine 4 was set to idle, and an computerized shutdown adopted. FO/2 confirmed the shutdown by urgent the Engine 4 Grasp and Hearth pushbuttons.
From the cockpit, the crew had no visibility of the engine harm. It was solely when a cabin crew member introduced up a passenger’s smartphone photograph that the size of destruction grew to become clear. FO/1 returned to the flight deck to help and personally inspected the engine from the higher deck, noting harm to the slats and minor vibrations within the flaps. After the inspection, the crew started evaluating their choices for diversion.
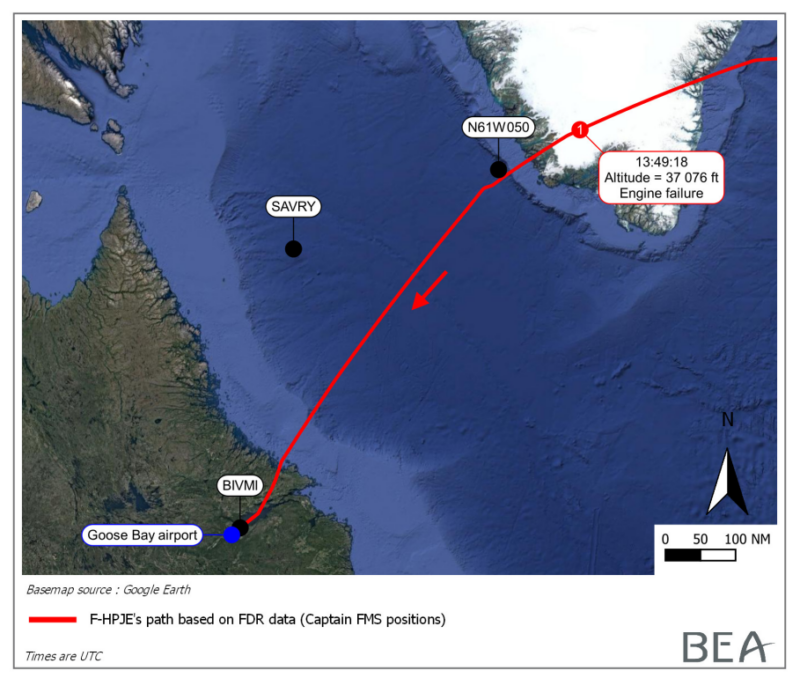
Diversion to Goose Bay
Though the plane initially maintained stage flight at FL370, airspeed started to fall from 277 knots to 258 knots within the first minute and a half after the engine failure. Conscious of the gradual deceleration, the captain initiated a drift-down to the engine-out most altitude (EO MAX FL 346) computed by the flight administration system. The crew needed to pause ECAM procedures throughout every descent step, stabilizing at FL360, then FL350, FL330, FL310, and at last at FL270, the place a secure steadiness between thrust and pace was reached.
The three remaining engines have been pushed to Most Steady Thrust (MCT) to take care of efficiency. At FL270, the plane stabilized at 279 knots indicated airspeed, and a secure cruise was maintained.
About 5 minutes into the descent, Gander Oceanic Management famous the plane’s deviation from its cleared altitude and despatched a CPDLC message: “ATC NOW SHOWS YOU FL330. IS THERE A PROBLEM?” Moments later, Air France Flight 66 declared a Mayday, each by way of relay from one other plane and thru direct radio contact on 132.37 MHz. Gander ATC responded swiftly and commenced aiding with route clearance.
The crew evaluated their diversion choices in coordination with Air France’s operations heart. Whereas Kangerlussuaq Airport in Greenland was nearer, the crew selected to divert to CFB Goose Bay (YYR) in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. Elements influencing this choice included the captain’s prior expertise with Goose Bay, its method setting, and its longer, better-equipped runway, deemed extra appropriate for dealing with an A380 in irregular situations.
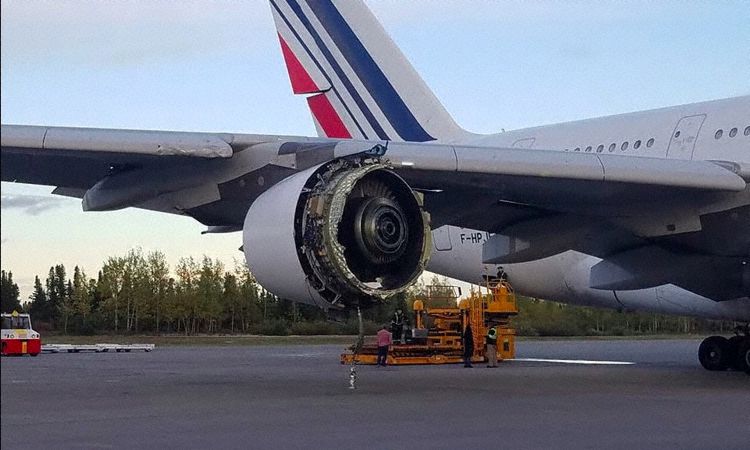

Touchdown in Goose Bay
Because the plane neared Goose Bay, it was cleared for the RNAV GNSS method to Runway 26. At 1,000 toes above floor stage, the captain disengaged the autopilot and the flight director and accomplished a handbook touchdown. At 15:42 UTC, Air France flight 66 touched down easily. Whereas taxiing in Goose Bay, the plane stopped a number of occasions as airport workers eliminated engine particles discovered alongside the runway.
Though secure on the bottom, the saga wasn’t fairly over. Goose Bay, a distant navy airport, was not geared up to deal with 500+ worldwide passengers. Immigration capability was overwhelmed, and lodging was restricted. Whereas some passengers have been allowed into the terminal, most remained onboard. Meals have been served on the plane, and the captain personally addressed the passengers in teams of fifty, explaining the state of affairs and the following steps.
Various flights have been organized, and by 08:10 on October 1, all passengers had disembarked, practically 17 hours after touchdown. Regardless of the extraordinary circumstances, there have been no accidents, and the crew’s calm, decisive actions ensured everybody reached security.
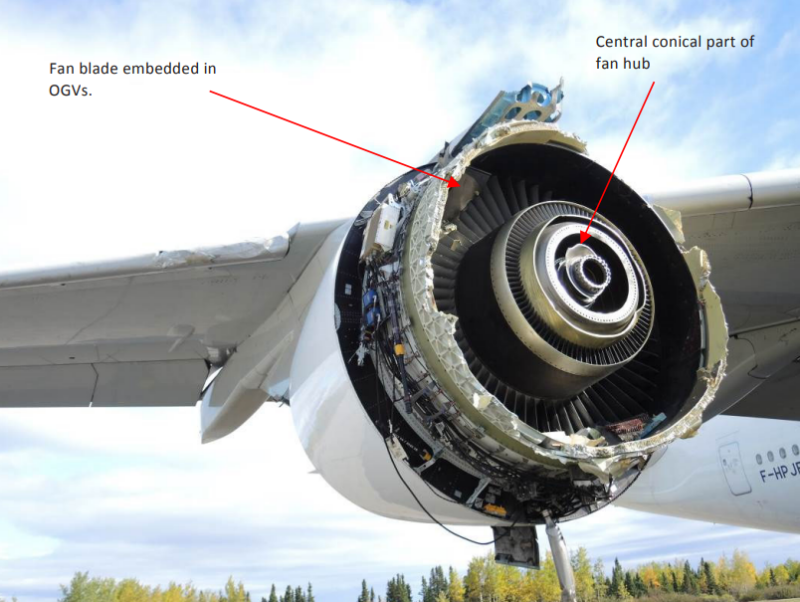

Plane Harm
Following the emergency touchdown at Goose Bay, preliminary inspections of Air France A380 revealed in depth harm to the quantity 4 engine and several other areas of the correct wing. Regardless of the severity of the in-flight engine failure, the plane had landed safely, and no structural harm had compromised the cabin or vital management methods.
Many of the engine’s ahead construction had been utterly destroyed or torn away. Lacking parts included the fan hub’s main elements, practically all the fan blades, the air inlet cone, and each engine cowlings. Over 2.5 meters of the air inlet part had indifferent throughout flight.
Furthermore, inspectors famous that giant parts of the fan case isogrid had disintegrated and peeled outward in a petaled sample between the 4 o’clock and 6 o’clock positions and the 8 o’clock and 12 o’clock positions. The central conical part of the fan hub remained connected to the engine’s low-pressure turbine shaft, however the hub itself had fractured alongside practically its complete circumference and was locked in place, unable to rotate. The fracture floor exhibited a matte, granular texture, per chilly dwell fatigue, a uncommon sort of failure initiated by gradual crack progress beneath low stress at excessive altitude.
Particles from the engine was discovered embedded inside the engine nacelle and on the runway, together with fan blade fragments, items of the entrance cone, structural honeycomb panels, and even attachment bolts. One fan blade fragment was found lodged inside the outlet information vanes (OGVs), which highlights the acute inside forces at play in the course of the breakup.
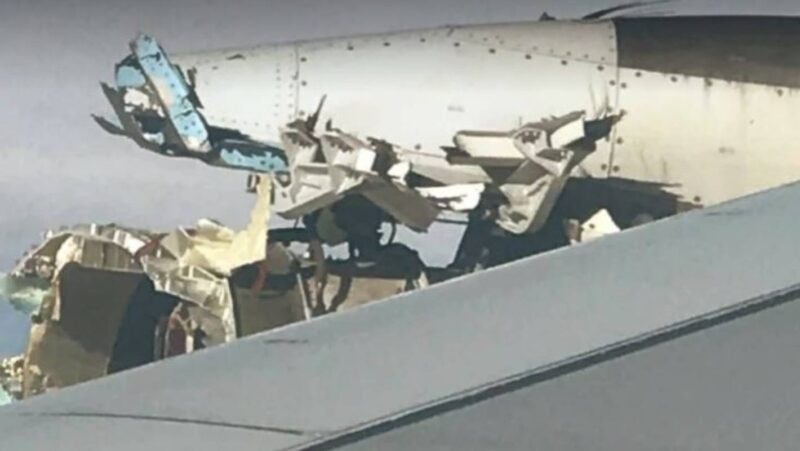

Wing and Airframe Harm
Whereas the uncontained failure despatched giant engine fragments flying in a number of instructions, the A380’s construction held agency. A number of impression marks and deformations have been recognized on the wing floor and the nacelle pylon supporting engine No. 4, indicating contact with indifferent engine elements.
Harm prolonged to the forefront slats, wing flaps, and aileron assemblies. Moreover, the flap rail fairings and parts of the trimmable horizontal stabilizer confirmed indicators of minor impression. Regardless of this, not one of the particles penetrated the cabin or gasoline tanks, and no lack of flight management methods occurred.
Based on the ultimate accident report, no different areas of the plane have been affected past these detailed above. The cabin remained sealed and undamaged, and there was no reported harm to passengers or crew. Whereas the harm was substantial, it remained localized to the engine construction and surrounding wing surfaces.

Investigation and Findings
The investigation was led by France’s BEA (Bureau d’Enquêtes et d’Analyses) with assist from the NTSB, Transport Canada, Airbus, and Engine Alliance (a three way partnership between GE and Pratt & Whitney).
The elements more likely to have contributed to the accident embrace:
Engine designers’/producers’ lack of expertise of the chilly dwell fatigue phenomenon within the titanium alloy, Ti-6-4;
Absence of directions from the certification our bodies about taking into consideration macro-zones (i.e., colony of equally oriented alpha grains) and the chilly dwell fatigue phenomenon within the vital elements of an engine, when demonstrating conformity;
Absence of non-destructive means to detect the presence of bizarre macro-zones in titanium alloy elements;
A rise within the threat of getting giant macro-zones with elevated depth in giant Ti-6-4 forgings resulting from larger engines, and specifically, larger followers.
Furthermore, the investigation into the failure later pinpointed the foundation trigger as a subsurface manufacturing anomaly within the titanium alloy fan hub, which had developed a fatigue crack that grew slowly over time.
The incident prompted a wide-reaching security response from Airbus, Engine Alliance, and regulatory authorities, resulting in emergency inspections of comparable engine fashions put in on different A380s worldwide.

Aftermaths
Air France initially thought-about ferrying the A380 again to Europe with a substitute engine shell, one which was inoperable and used solely for weight and steadiness functions. Because of the distinctive configuration and security issues of flying with a non-functional engine, such a flight required particular working procedures and simulator coaching by the flight crew.
Nevertheless, this plan was later revised. On December 6, 2017, the plane was efficiently ferried from Goose Bay Airport again to Paris Charles de Gaulle Airport utilizing 4 totally operational engines, with an Air France crew on the controls.
In the meantime, the broken engine was flown to East Midlands Airport in the UK, the place Common Electrical examined the engine from the twenty third to the twenty fifth of November 2017. This evaluation grew to become a key a part of the broader investigation into the reason for the fan hub failure.
After months of inspections and structural repairs, F-HPJE was returned to industrial service on January 15, 2018. It remained in operation till Could 2020, when Air France formally retired its A380 fleet amid the dramatic downturn in air journey attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic. The plane’s remaining flight came about on April 28, 2020, when it was ferried from Paris to Tarbes–Lourdes–Pyrénées Airport (AF371V), the place it joined two different retired Air France A380s and several other ex-Singapore Airways items in long-term storage.
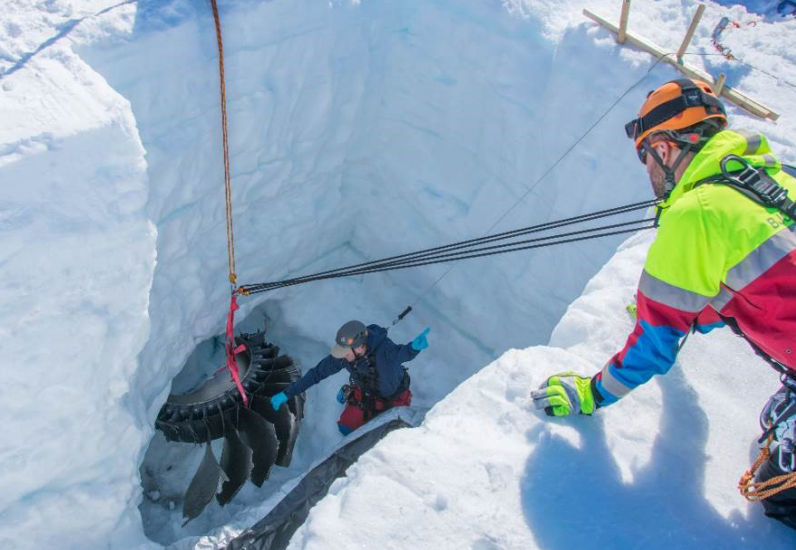
In a notable postscript, the lacking fan hub fragment, which had separated from engine No. 4 and fallen onto the Greenland ice sheet, was lastly recovered after a prolonged and complicated operation. The search effort spanned 4 phases over 20 months and culminated in a profitable aerial and floor restoration on 29–30 June 2019, offering essential forensic proof for investigators.
Sources: BEA, Wikipedia





