Airworthiness is a type of components of pilot life we are likely to take without any consideration. We verify paperwork and log out on inspections virtually out of behavior. As soon as we see the airworthiness certificates, we feature on with our preflight verify and not using a second thought.
However for a superb pilot, following the foundations isn’t sufficient. They attempt to perceive why we’ve these guidelines within the first place.
So collectively, let’s dig deeper into what “airworthy” actually means, who’s answerable for preserving an plane that method, and the way these necessities form our selections within the cockpit.
Key Takeaways
An airworthy plane conforms to its sort design and is in a situation for protected operation.
The principles for airworthiness are written in Title 14 of the Code of Federal Rules.
Make sure that your plane’s required inspections are up-to-date.
Pilots are answerable for figuring out their plane’s airworthiness earlier than flight.
What Does Airworthiness Imply?
We pilots have our licenses and scores to certify that we’re match to fly. For plane, they’ve airworthiness. It’s the authorized and sensible commonplace that tells us an plane is actually accredited for flight.
America federal authorities publishes a Code of Federal Rules (CFR). This code describes 50 titles for areas topic to regulation.
Title 14 accommodates the foundations masking aeronautics and area, which we name the Federal Aviation Rules, or FARs. That is the place we discover the premise of airworthiness.
How does Title 14 outline airworthiness? Beneath 14 CFR 3.5(a), an “airworthy” plane conforms to its sort design and is in a situation for protected operation. You could find the main points pertaining to airworthiness directives underneath 14 CFR half 39.
In different phrases, two key situations should be met earlier than an plane is taken into account airworthy. Let’s speak about them.
The Two Situations for Airworthiness
Conformity to Kind Design
Whereas it appears apparent, your plane should first be what it’s.
These specs and extra are all specified by your plane’s Kind Certificates Information Sheet (TCDS). Right here, you’ll discover the proper construction, techniques, and security tools as accredited to your particular plane.
So should you make any adjustments, they should be backed by FAA‑accredited knowledge. These could possibly be from Supplemental Kind Certificates (STCs) or FAA Discipline Approvals.
Situation for Protected Operation
However even when your plane matches completely in its design sort, it could possibly turn out to be unsafe should you don’t maintain it. Is your plane well-maintained? It must be free from injury, corrosion, or mechanical points that might put security in danger.
This implies all elements in your plane should operate reliably. It should move its scheduled inspections—annual, 100‑hour, or others—as required.
Regulatory Foundation for Airworthiness

We’ve established that 14 CFR is our basis of airworthiness. However the place is that this mentioned, precisely?
Within the U.S., airworthiness guidelines are unfold throughout a number of components of the code. Collectively, they make the inspiration of how plane are licensed, maintained, and operated.
To seek out how plane and components earn their certification, learn via Half 21. It units procedures for sort certificates, manufacturing certificates, and design approvals.
Are you on the lookout for upkeep guidelines? Learn via Half 43.
14 CFR Half 91 covers operational guidelines for flying licensed plane. It talks about inspections like annual and 100‑hour checks.
The authority of the FAA to concern Airworthiness Directives (ADs) is written in Half 39. These directives are issued to repair identified issues of safety in plane or elements.
Airworthiness Certificates
As a result of not all plane are made and used the identical method, the FAA points two forms of airworthiness certificates: commonplace and particular.
Which one does your plane want? Properly, it’ll rely upon its design and meant use. Let’s speak about it.
Normal Airworthiness Certificates
A normal airworthiness certificates applies to plane that maintain sort certification within the following classes:
Regular
Utility
Acrobatic
Commuter
Transport
Manned Free Balloons
Particular Lessons of Plane
Particular Airworthiness Certificates
The particular airworthiness certificates covers plane that don’t meet necessities for normal certification. This consists of classes similar to:
Main
Restricted
Restricted
Mild-Sport
Provisional
Experimental
Particular Flight Permits
For instance, the experimental certificates covers plane used for issues like analysis and improvement, displaying compliance with rules, crew coaching, exhibition, air racing, or market surveys.
However, a restricted certificates is given to plane used for particular jobs similar to crop dusting, towing banners, or aerial surveying.
Validity
How lengthy is the validity of an airworthiness certificates? Whereas they’ve completely different makes use of, each commonplace and particular certificates stay legitimate underneath the identical situations.
Your plane must:
Conform to the accredited design.
Be in a protected working situation.
Have preventative upkeep and alterations be carried out underneath 14 CFR components 21, 43, and 91.
Be registered in the US.
So long as these necessities are met, the certificates stays lively.
Pilot and Proprietor/Operator Obligations

Pilot-in-Command (PIC) Obligations
14 CFR 91.7(b) states that, “The pilot answerable for a civil plane is answerable for figuring out whether or not that plane is in situation for protected flight”.
Discover how this doesn’t point out a mechanic or an operator. In keeping with the regulation, this duty is all as much as you.
So, how are you going to meet this responsibility? You could fastidiously evaluation upkeep logs, flight manuals, and required inspection information. Then, carry out an intensive preflight inspection guided by the AFM/POH guidelines.
Hopefully, you’ve been doing these completely earlier than each flight.
If any unairworthy mechanical, electrical, or structural situation happens within the air, you might be required by regulation to discontinue the flight. In such conditions, clever decision-making and security are your high priorities.
Proprietor/Operator Obligations
As outlined in 14 CFR 91.403(a): “The proprietor or operator of an plane is primarily answerable for sustaining that plane in an airworthy situation, together with compliance with half 39.”
What does this imply? When you’re an proprietor or operator, the first duty for preserving the plane airworthy falls on you.
According to that, you must also hold clear information of any upkeep, repairs, or adjustments as required by 14 CFR 91.417. You must also observe all relevant Airworthiness Directives (ADs) inside the deadlines.
Required Plane Documentation (ARROW)

You’re most likely conversant in the acronym ARROW. This can be a helpful mnemonic for the paperwork that have to be onboard earlier than each flight.
However why should we’ve these paperwork within the first place? And what does regulation say about these necessities? Let’s discover out.
Airworthiness Certificates (A)
Do not forget that the airworthiness certificates proves that your plane meets design necessities. It additionally ensures that the plane has been evaluated by authorities and regarded protected for flight.
Your plane’s present airworthiness certificates should be on board and displayed on the cabin or cockpit entrance. It additionally must be legible to passengers or crew upon boarding.
Registration Certificates (R)
For U.S. plane, nobody is allowed to function a civil plane except it carries correct proof of registration on board. This implies your plane should have a sound U.S. registration certificates issued to the proprietor.
In any case, the important thing requirement is that your U.S.-registered plane should have legitimate U.S. registration documentation throughout flight.
It’s additionally essential that your plane’s registration be present. The certificates used to run out each three years, although current adjustments now lengthen it to seven years, so verify your present renewal date fastidiously.
Radio Station License (R)
When you fly internationally or want to speak with international stations, you have to carry a present FCC-issued radio station license on board. Having one allows you to function your radio tools overseas, and it’s legitimate for ten years. However should you’re solely flying inside the U.S., a radio station license shouldn’t be required.
Working Limitations (O)
Working limitations are one other obligatory doc. They outline the accredited and protected operational boundaries of your plane.
The place can you discover them? They’re normally within the POH/AFM, cockpit placards, and instrument markings. Your plane’s working limitations are there as a reference for the licensed security margins of your plane.
Inspectors verify for them routinely, and failing to have them onboard can result in severe penalties. These limits should be present and accessible onboard; in any other case, your flight shouldn’t be legally permitted.
Weight and Stability Information (W)
Since they’re established as working limitations, present weight and stability documentation should even be on board your plane. This could embody any current adjustments made to have an effect on weight and stability.
Keep in mind the impression of weight and stability in your plane’s efficiency. 14 CFR 91.9 requires you to adjust to the working limitations specified within the accredited Airplane Flight Handbook/Pilot’s Working Handbook.
These limits make sure that the airplane can function correctly with out overloading any a part of the construction. If particular loading patterns may have an effect on security, these must also be clearly outlined.
Upkeep and Inspection Necessities
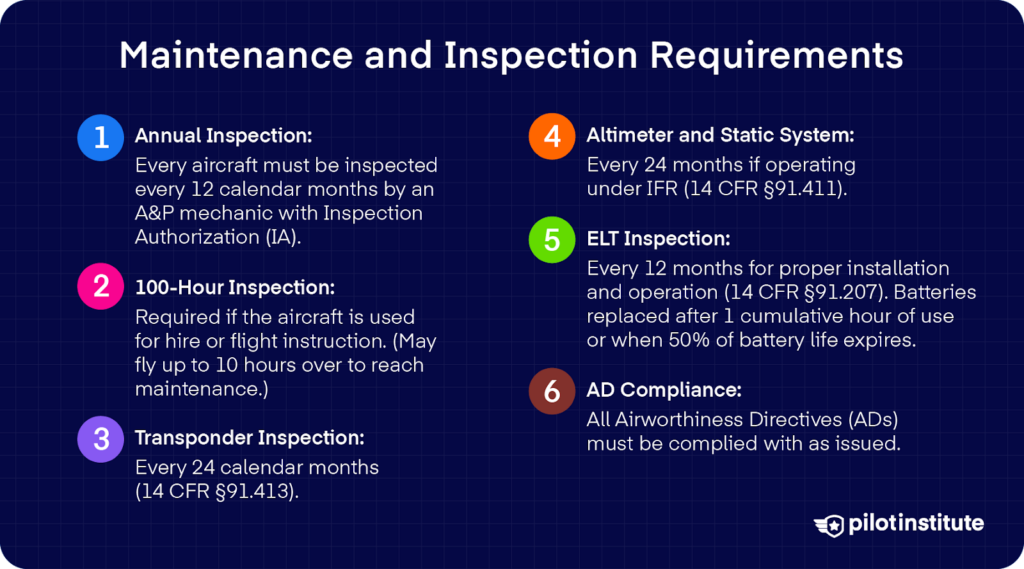
To ensure each plane within the air is in form to fly, they have to be recurrently inspected and move these inspections.
Each plane should endure a full annual inspection no later than 12 calendar months after the final one.
Who ought to do that inspection? An A&P mechanic with Inspection Authorization (IA) should conduct this thorough verify to legally return the plane to service.
In case your plane is used for rent or flight instruction, it should get a 100-hour inspection each 100 flight hours. You’re allowed as much as 10 further hours to achieve the inspection facility, however these hours depend towards the subsequent interval of the 100-hour inspection.
Transponder, Altimeter, and Pitot-Static Inspections
Beneath Instrument Flight Guidelines (IFR), you have to have your altimeter, static system, and computerized altitude reporting system examined each 24 calendar months.
On high of that, your transponder must be inspected on the similar 24‑month interval for any operation in managed airspace requiring a transponder. This must be achieved by a certified restore station.
Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT) Inspection
Your Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT) should even be inspected each 12 calendar months. The inspection consists of checks for correct set up, corrosion, practical controls (together with the crash sensor), and sign power.
Your ELT has batteries that have to be changed or recharged when 50% of their helpful life is used, or after one hour of transmitter operation, whichever comes first.
Airworthiness Directives (ADs)
What Are ADs?

Generally, points in plane, engines, propellers, or associated tools solely present themselves after they’ve been rolled out to the market.
To handle these issues, the FAA enforces Airworthiness Directives underneath Half 39. These directives take impact when the FAA finds a security concern in a design that doubtless impacts different related plane.
Compliance With ADs
How will you keep up to date? You possibly can verify FAA AD databases recurrently, evaluation notices from the producer, and keep in shut contact together with your upkeep personnel.
You possibly can even join e-mail supply of latest ADs and Particular Airworthiness Info Bulletins (SAIBs), primarily based in your plane sort and make.
When you adjust to the directives within the AD, you’ll should log it in your upkeep document. That entry ought to embody:
The AD quantity and revision date.
The tactic you used to conform.
The date and whole plane time at completion.
The signature with the certificates variety of the one who carried out the work.
Distinction Between ADs and Service Bulletins
Producers typically concern Service Bulletins (SBs) to tell operators about potential points, upgrades, or safety-related issues.
However how are they completely different from ADs? Service bulletins are producers’ suggestions. They don’t seem to be legally binding except they’re:
Included into an Airworthiness Directive (AD).
Are a part of the FAA-approved Airworthiness Limitations part of a upkeep handbook.
Are a part of an FAA-approved inspection program.
However despite the fact that they’re technically not obligatory, it’s good observe to deal with an SB the identical method you’d an AD.
Inoperative Tools and Minimal Tools Lists (MEL)

14 CFR 91.213 was written in order that despite the fact that completely different plane have completely different tools, they a minimum of have the entire necessities to function safely.
Chances are you’ll function an plane with lacking or inoperative tools, however solely underneath two situations:
First, you need to use a FAA‑accredited Minimal Tools Listing (MEL) particular to that plane.
And second, should you don’t have an MEL, you have to observe the provisions underneath 14 CFR 91.213(d). The inoperative or lacking tools should not be required by the sort certificates, the plane’s tools checklist, or any relevant efficiency tools checklist.
It additionally should not be required by 14 CFR 91.205 or an Airworthiness Directive.
There may additionally be further tools wanted relying in your sort of flight. So be sure that any inoperative tools additionally adjust to the Sorts of Operation Tools Listing (KOEL), in case your plane has one.
The KOEL signifies the precise tools you’ll want for various kinds of operation, similar to Day‑VFR, Evening‑VFR, IFR, or flight into identified icing. You’ll sometimes discover this in your plane’s POH or AFM.
But when your plane doesn’t have a proper KOEL, then solely the working limitations within the POH apply.
Minimal Tools Lists (MELs)
What’s an MEL? It’s a doc tailor-made to a particular plane itemizing which objects might be inoperative whereas nonetheless having the ability to fly legally.
It’s constructed from the Grasp Minimal Tools Listing (MMEL) offered by the FAA and developed along with the producer. The MEL must get FAA approval and a Letter of Authorization (LOA). With out the accredited MEL and LOA, you have to adjust to 91.213(d) as a substitute.
As soon as accredited, the MEL capabilities like a Supplemental Kind Certificates.
When utilizing the MEL, you’ll have to observe the procedures strictly. Make sure that the elements your plane does have are all in good working situation earlier than taking off.
Procedures With out an MEL
Now, in case your plane doesn’t have an MEL, you’ll have to observe the rules written in 14 CFR 91.213(d). So, how are you going to be certain you’re flying legally?
In keeping with the rule, the malfunction should be eliminated or deactivated. It should even be clearly marked with an “Inoperative” placard.
If the elimination or deactivation of the tools constitutes upkeep, an entry describing the work carried out should be made within the upkeep information in accordance with 14 CFR 43.9.
And at last, a pilot who’s certificated and appropriately rated for the plane, or an individual who’s certificated and appropriately rated to carry out upkeep on the plane, should decide that the inoperative merchandise doesn’t current a hazard to the flight’s security.
Figuring out Airworthiness Earlier than Flight
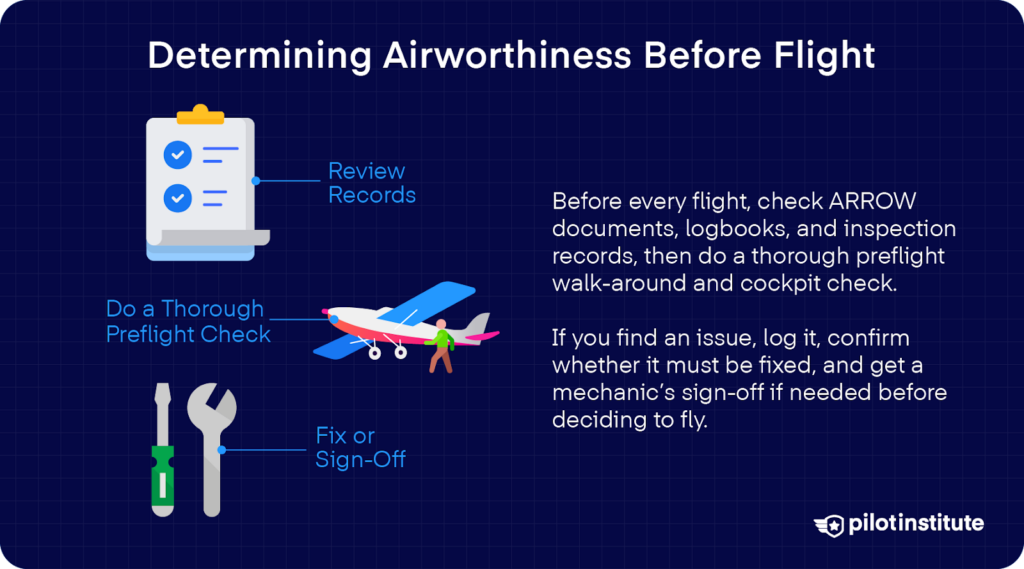
You’re simply as answerable for your plane’s situation—and that begins earlier than each flight. Start with the ARROW paperwork, then evaluation the logbooks for the airframe, engine, propeller, and home equipment.
Test if all inspections (annual, 100-hour, ADs, and upkeep) are present. Have a look at the date, whole time, and sort of the final inspection, together with any service bulletins.
Make sure that the entry is signed with the mechanic’s identify, certificates quantity, and sort. Lastly, verify there aren’t any lacking signatures and that deferred objects are correctly documented.
Preflight Inspection
As soon as that’s achieved, it’s time to your walk-around. Every pilot has their very own system relying on their model. However to maintain issues organized, you may divide this into two components.
After you head to your plane, when you’re nonetheless exterior, start with an exterior verify. You must stroll across the plane and examine structural areas. Can you see any injury, corrosion, or put on?
Test the tires, brakes, and touchdown gear for situation. And as you verify the gasoline and oil ranges, verify for any leaks and correctly safe the caps.
When you get contained in the cockpit, take a look at that every one devices, avionics, switches, and controls are functioning appropriately. Ensure that the circuit breakers are all in.
Determination-Making
Based mostly on what you’ve gathered to date, you’re now outfitted to make an knowledgeable choice about your plane’s airworthiness. Do not forget that this consists of whether or not the plane conforms to its sort design.
So, what should you spot a difficulty? Cease and assess the state of affairs instantly. Log the discrepancy clearly within the upkeep or discrepancy log so it’s formally documented.
If the element in query is required by rules (like for sort certification, tools lists, ADs, or MEL), then it must be fastened earlier than you fly.
However, if it’s non-essential for that flight, it is best to observe the steps we mentioned underneath 14 CFR 91.213(d).
After repairs or deactivation are accomplished, it ought to get a sign-off from a certified mechanic. Solely then is it protected and authorized to proceed.
However with that mentioned, airworthiness is only one think about making a sound go/no-go choice. You must also think about the climate, your proficiency, and plane efficiency limitations.
Penalties of Working an Unairworthy Plane

Whether or not they have been conscious of it or not, some pilots have flown unairworthy plane up to now. And oftentimes, their option to proceed has led to some severe penalties.
Security Dangers
The principle goal of certifying airworthiness is to make sure all plane within the air are in good and protected working situations. Flying with out it robotically signifies that you’re placing your security in danger.
Your possibilities of operating into mechanical failure, lack of management, or some other catastrophic accident enhance considerably. Any points that may’ve been caught throughout an inspection go unchecked, and that makes it more likely for one thing to go unsuitable in flight.
If this occurs on the worst doable time, you’ll have little to no margin to recuperate. This doesn’t simply endanger you and your passengers; it additionally places folks on the bottom in danger.
Authorized Implications
However even should you handle to land safely, you’re not off the hook simply but. Legally talking, flying an unairworthy plane is a violation of FAA rules.
While you get caught—which you almost certainly would—the FAA has a variety of enforcement instruments it could possibly use.
This may embody civil penalties (fines), or the suspension or revocation of your pilot certificates. In extreme conditions, regulation enforcement and felony expenses are an actual risk.
Influence on Insurance coverage and Monetary Legal responsibility
Flying an unairworthy plane is harmful and unlawful. However on high of those, additionally it is costly.
Insurance coverage insurance policies usually embody strict clauses that require compliance with airworthiness requirements. When you’ve flown an unairworthy plane, insurance coverage firms might refuse to honor claims.
Consider the prices you’ll should shoulder out of pocket. You’ll have to pay for repairs, liabilities from passenger or third-party accidents, and authorized protection bills.
Conclusion
The aviation business wouldn’t be as protected as it’s now with out airworthiness. It ensures that each plane within the sky—from a tiny Cessna to an infinite Boeing—meets the best requirements of security.
Whereas it might appear overwhelming, the FAA has outlined airworthiness for us as clearly as doable. After studying via the foundations, one factor turns into evident: Airworthiness is a group effort.
The FAA, mechanics, operators, and pilots alike are answerable for making a protected and productive airspace.





