Pilots continually be careful of the cockpit home windows, and air site visitors management screens site visitors within the airspace.
However what occurs if the pilots can’t see incoming site visitors and ATC in some way misses a possible battle?
When all else fails, TCAS will warn you and information you to security. We’ll clarify what it’s, the way it works, and the way it will help preserve your plane secure.
Key Takeaways
TCAS entails plane transponders interrogating one another to foretell a collision course.
A possible battle triggers a Site visitors Advisory (TA). This might escalate to a Decision Advisory (RA).
TAs are solely an alert. RAs give specific coordinated directions to keep away from a collision.
ACAS X might be dramatically extra succesful than present variations of TCAS.
What Is TCAS?
TCAS (Site visitors Collision Avoidance System) is an plane security system designed to scale back the chance of mid-air collisions. Whereas TCAS doesn’t maneuver the plane itself, it offers alerts and steering to pilots when one other plane comes too shut for consolation.
Why is TCAS so vital?
It’s true that air site visitors controllers on the bottom preserve watch over plane of their airspace and ensure they keep safely separated.
Pilots themselves scan for site visitors by searching the cockpit home windows.
Nevertheless, people and floor radar programs usually are not infallible. Miscommunications or undetected errors can and do happen.
TCAS serves as a last-resort backup. It really works independently of air site visitors management and may detect conflicts even when controllers miss them or pilots don’t see them in time.
Why Was TCAS Developed?
The push for an airborne collision avoidance system dates all the way in which again to the Nineteen Fifties.
In 1956, a United Airways DC-7 and a TWA Constellation collided over the Grand Canyon, killing all on board. The dimensions of the tragedy prompted the aviation business to discover expertise that might stop mid-air collisions.
A giant problem was getting two plane to keep away from one another cooperatively. Early ideas couldn’t reliably get each plane to agree on avoidance maneuvers. It grew to become clear that any viable system would want some type of communication between the plane.
By the Nineteen Seventies, consideration turned to utilizing the indicators from transponders to create a collision avoidance system.
Transponders have been gadgets that had develop into frequent on many plane to make them seem on ATC radar. However how may they assist with collision avoidance?
Transponders already transmit an plane’s sign after they reply to radar. An onboard system may ship its personal interrogations and detect these replies.
In 1981, the FAA formally determined to pursue what ultimately grew to become TCAS.
How TCAS Works
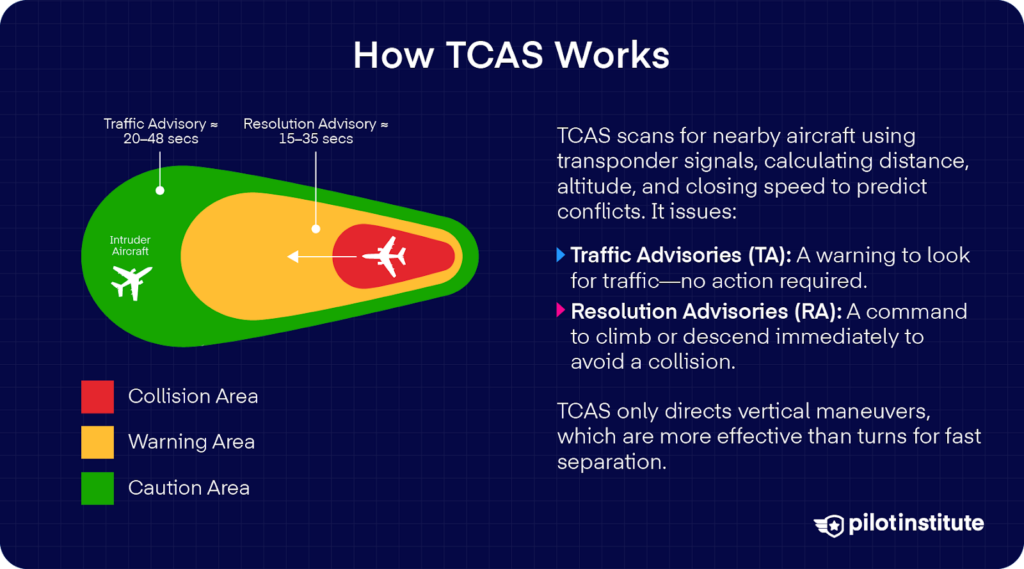
To know how TCAS works, let’s break it down step-by-step.
Each TCAS-equipped plane actively sends radio indicators asking who’s on the market and listens for replies. These indicators interrogate the transponders of different plane close by.
A transponder responds with identification and altitude knowledge when it receives a radar or TCAS sign.
So, when your TCAS pings the realm, any plane inside vary that has its transponder on will reply with its presence and altitude.
TCAS computes the gap to the opposite plane by timing how lengthy the reply takes.
It will get the altitude distinction by evaluating the opposite plane’s reported altitude to your personal.
Utilizing repeated interrogations, TCAS can monitor the opposite plane’s path and shutting velocity.
With this data, the TCAS laptop repeatedly predicts the long run path of close by plane relative to your personal. When the time of closest method falls under sure ranges, TCAS points alerts.
Alerts and Advisories
TCAS has two important alert ranges comparable to the 2 kinds of advisories:
Site visitors Advisory (TA)
A TA is a preliminary warning. It’s TCAS merely supplying you with a heads-up.
The system will announce “Site visitors, site visitors,” and in your cockpit show the intruding plane might be highlighted (usually in yellow).
The show additionally reveals the opposite plane’s relative altitude. For instance, “+05” signifies the site visitors is 500 ft above you. If the opposite plane is climbing, you’ll see a small arrow pointing upwards subsequent to the quantity. The arrow factors downward if the site visitors is descending.
A TA doesn’t inform you learn how to maneuver; it’s advisory solely. The right pilot response is to start out on the lookout for the site visitors and be prepared if an evasive maneuver turns into obligatory. You’re not presupposed to deviate from ATC’s directions on a TCAS site visitors advisory.
Decision Advisory (RA)
If the state of affairs worsens and the gap closes quickly, TCAS will challenge a Decision Advisory. That is an instruction that have to be adopted instantly.
An RA triggers at about 15 to 35 seconds to the projected collision level. At this stage, a mid-air collision is imminent until you’re taking motion. TCAS will command an escape maneuver within the vertical path.
For instance, you would possibly hear an audio alert say “Climb, climb!” or “Descend!”. Or it could challenge instructions like “Monitor vertical velocity” or “Keep vertical velocity” if solely a slight adjustment is required.
You additionally get visible cues on the cockpit show, often on the vertical velocity indicator (VSI). The areas marked crimson on the VSI present climb or descent charges that may put you on a collision course. Inexperienced markings present the climb or secure climb, or descent charges. TCAS RAs can solely inform you to climb or descend.
That is by design. In fast-moving plane, a sudden flip left or proper may not be quick sufficient to create separation. Vertical maneuvers are extra predictable and efficient for speedy separation, so TCAS focuses on these.
Elements of TCAS
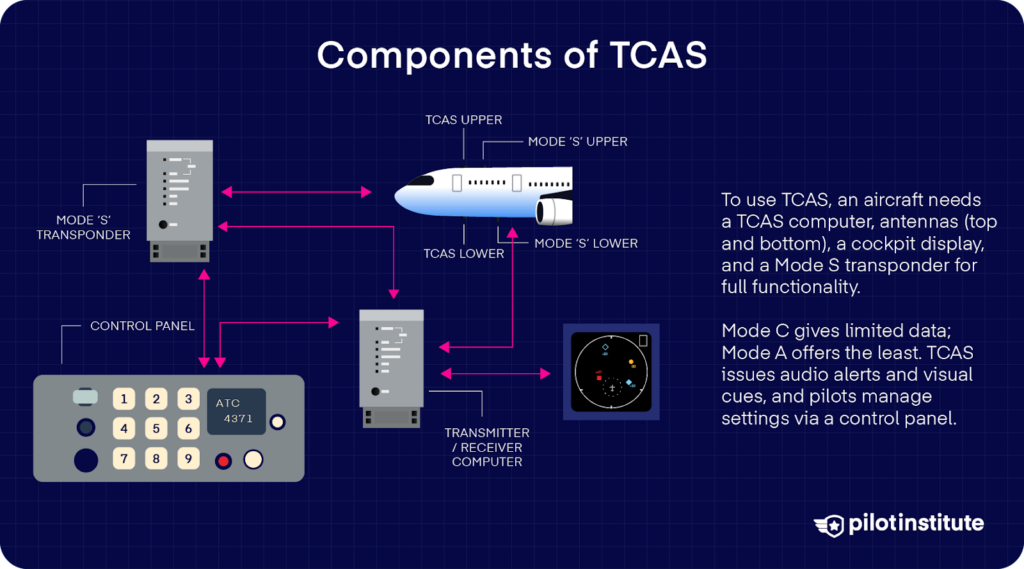
What does an plane want to make use of TCAS?
TCAS Pc/Processor: Normally put in within the avionics bay, the TCAS laptop sends out interrogations, listens to replies, tracks as much as dozens of plane, and decides when to challenge TAs or RAs.
Transponder: TCAS works in tandem with the plane’s transponder. There are various kinds of transponders, with every having completely different capabilities. Trendy TCAS II programs require you to have a Mode S transponder.
Mode S transponders enable direct TCAS communication between two plane.
You probably have a Mode C transponder, it will possibly solely report altitude and can’t present TCAS functionality. This kind can solely present site visitors advisories or uncoordinated RAs to the opposite plane.
Mode A transponders are very primary and may’t even report altitude. This kind of transponder permits different plane to determine your place however not your altitude.
TCAS Antennas: Plane often use two antennas for TCAS. One is often mounted on high of the fuselage and one on the underside. These antennas enable TCAS to ship and obtain indicators in 360-degree protection across the plane in each horizontal and vertical instructions.
Cockpit Shows: Trendy plane sometimes combine TCAS site visitors proper into their navigation show within the cockpit. This show reveals the place the opposite plane is in relation to you. For instance, “Site visitors at 2 o’clock, 3 miles, 500 ft under” might be drawn roughly in that relative path on the display screen.
The coloured bands seem on the VSI solely throughout an RA. Newer glass cockpits could present this steering as a flight director cue on the first flight show (PFD)
Aural Alerts: A synthesized voice will name out “Site visitors, site visitors” for a TA, and specific directions like “Climb, climb” or “Descend, descend now!” for RAs. They’re designed to be attention-grabbing and unambiguous.
Management Panel/Switches: Pilots can change TCAS settings by means of a management panel. That is usually a part of the transponder management head, however could be a separate TCAS management unit. Right here, they’ll set the system’s mode.
“Standby” turns the TCAS surveillance off. It’s used on the bottom or if the system shouldn’t be wanted.
“TA/RA” is the traditional operational mode in flight, wherein the system points each site visitors advisories and backbone advisories as wanted.
“TA Solely” mode provides you site visitors alerts however no computerized RAs. Some fashions enable adjusting the altitude filter of displayed site visitors to give attention to threats above or under.
Forms of TCAS Techniques
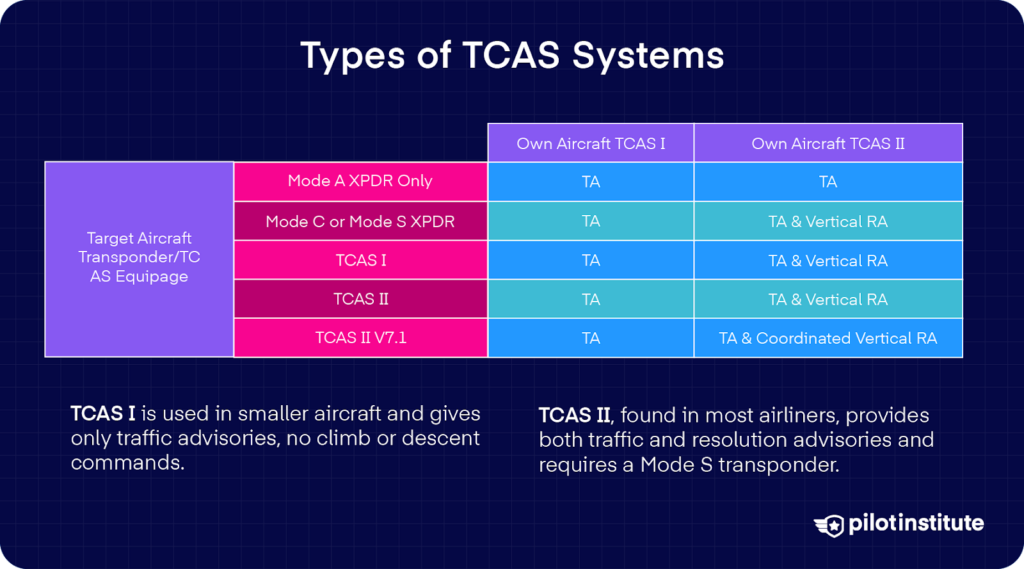
TCAS I
It is a easier type of the Site visitors Collision Avoidance System, sometimes present in smaller plane. This contains some enterprise jets, turboprops, and regional airliners mandated to have it. You possibly can even discover it as an elective system in small basic aviation plane.
TCAS I offers site visitors advisories solely and no decision advisories.
It is going to warn you of close by transponder-equipped site visitors that could be a menace, however it gained’t inform you to climb or descend. TCAS I leaves the avoidance maneuver as much as the pilot’s judgment.
Technically, TCAS I doesn’t require full Mode S functionality. It could possibly work with Mode C transponder replies because it doesn’t coordinate RAs. Nowadays, it’s possible you’ll come throughout fashions constructed by Garmin, Avidyne, or others for high-end GA plane.
TCAS II
TCAS II is the usual TCAS system utilized by most fashionable airliners. It contains coordination between plane and provides Decision Advisories.
TCAS II requires a Mode S transponder to work. You’ll discover completely different software program variations inside TCAS II. These variations don’t change how a pilot interacts with TCAS. They solely make small modifications to its programming.
TCAS III
TCAS III was a proposed superior model of TCAS that was meant to offer horizontal decision advisories along with vertical. The thought was that TCAS III would inform pilots to show left/proper or climb/descend or a mix, choosing the right route in 3D.
Analysis was completed on TCAS III within the late Eighties and 90s, however growing an algorithm that reliably handles horizontal maneuvers turned out to be extraordinarily complicated. TCAS III improvement was discontinued, and it didn’t enter common service.
Operation and Pilot Procedures
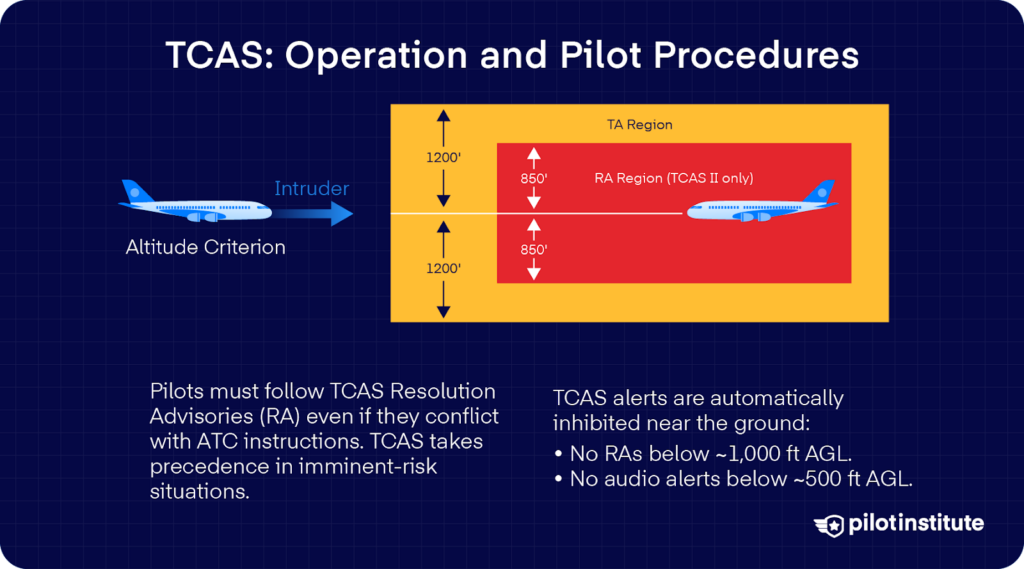
Having TCAS on board is one factor, however realizing learn how to use it accurately is equally vital. Pilots endure coaching for TCAS, and there are established procedures on how to answer its advisories.
Earlier than Flight / Regular Monitoring:
On the bottom, TCAS is often saved on Standby to keep away from nuisance alerts on the bottom. Pilots swap TCAS to TA/RA when lining up for takeoff.
TCAS retains monitoring site visitors all through the flight. You’ll see close by site visitors passing by in your show. TCAS gained’t warn you so long as the site visitors is safely separated, however seeing close by site visitors helps with situational consciousness. It additionally makes it simpler to identify site visitors when ATC requests it from you.
Receiving a Site visitors Advisory
The primary signal of potential hassle is the audible “Site visitors, site visitors” announcement. The intruder inflicting the TA will flip amber on the show to get the pilots’ consideration.
At this level, the pilots merely search for site visitors and put together to maneuver if wanted. One pilot often begins scanning visually within the path indicated, whereas the opposite screens devices.
A TA doesn’t imply you’re presupposed to deviate out of your cleared flight path. Probably the most you are able to do is concentrate if an RA follows and maybe double-check that you just’re flying accurately at your assigned altitude.
Responding to a Decision Advisory
If the intruding plane retains getting nearer, TCAS will escalate to a Decision Advisory. An RA means you must take speedy motion. The system will specify what to do by way of voice command and VSI shows.
Upon listening to an RA, the pilot process is to disconnect the autopilot and hand-fly the commanded maneuver.
Why not let the autopilot deal with it?
Autopilots aren’t programmed to observe TCAS RAs. Some newer plane, such because the A380, do have an automatic TCAS mode for autopilots, however that’s the exception. Usually, the pilot is meant to take management manually as a result of an RA could demand a faster response or extra abrupt maneuver than an autopilot would usually carry out.
If TCAS instructions “Enhance climb” or “Enhance descent,” it means the preliminary response wasn’t sufficient and a steeper change is required.
One pilot focuses on flying the RA maneuver whereas the opposite screens. As quickly as they’ll, the crew should inform air site visitors management that they’re deviating on account of a TCAS RA. Controllers gained’t attempt to override a TCAS maneuver.
In actual fact, you’re presupposed to observe TCAS directions even when ATC provides you the other command. The 2002 Überlingen mid-air collision occurred when one plane adopted TCAS instructions whereas the opposite obeyed the controller’s directions.
TCAS will announce “Away from battle” when the hazard has handed. At that second, pilots stage off after which inform ATC that they’re away from the opposite plane.
Usually, the complete TCAS RA episode lasts solely a handful of seconds from preliminary RA to clear-of-conflict.
Pilots apply TCAS encounters in simulators as a part of their coaching. The coaching emphasizes that in TCAS RA occasions, react first and ask questions later.
Inhibitions and Limitations
TCAS is programmed to cease giving alerts in sure situations routinely.
RAs are inhibited when the plane is lower than 1,000 ft above the bottom. This prevents harmful maneuvers throughout takeoff and touchdown.
Aural TAs and RAs are each inhibited under 500 ft above the bottom. This prevents distractions from nuisance alerts at this vital section of flight.
Even when TCAS isn’t routinely inhibited, there are conditions the place it will possibly’t allow you to.
If the opposite plane’s transponder is off or disabled, TCAS can’t see it.
Conversely, conditions like approaches in intently spaced parallel runways can have too many nuisance alerts. Pilots could flip off RA and swap to TA-only, following accredited procedures.
Regulatory Necessities and Requirements

The FAA has a algorithm explaining what sort of TCAS your plane wants based mostly on seat depend and Most Takeoff Weight.
Giant turbine plane weighing over 33,000 kilos or over 30 passenger seats should carry TCAS II.
Turbine plane with 10 to 30 passenger seats should have no less than TCAS I. TCAS II can also be allowed.
Giant piston plane over 33,000 lb should have TCAS I no less than, however they might use TCAS II.
At any time when TCAS II is used, it must be model 7.0+
All different U.S.-registered plane wouldn’t have to put in TCAS. This contains most general-aviation plane, gentle enterprise jets, helicopters, and gliders. In the event that they carry it voluntarily, it should keep on, and any RA have to be adopted.
Overseas airways flying in U.S. airspace observe the identical weight and seat guidelines.
Developments in Collision Avoidance
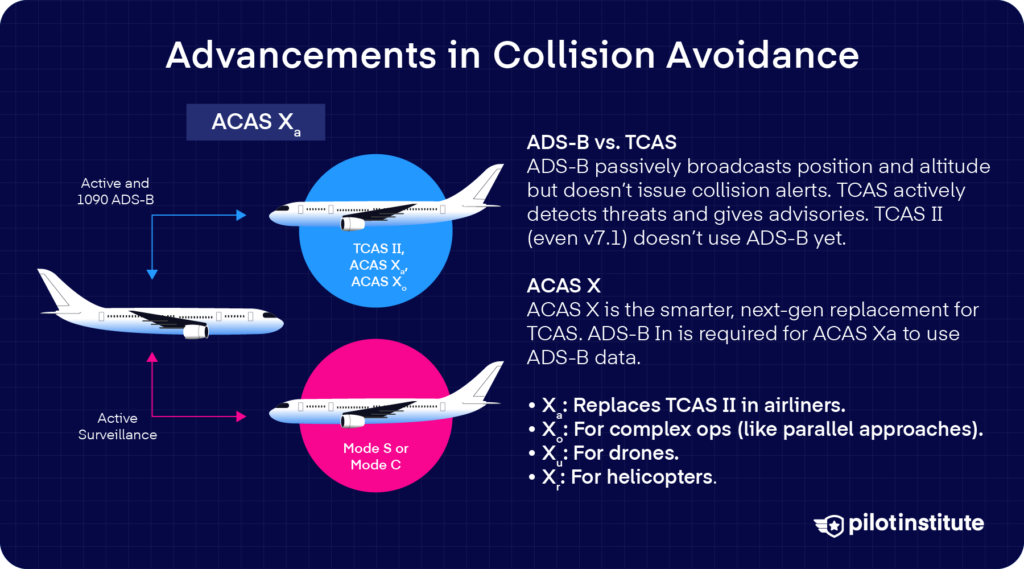
Integration with ADS-B
ADS-B stands for Automated Dependent Surveillance–Broadcast. It’s a system that enables plane to broadcast their place, velocity, altitude, and different knowledge to different plane and floor stations.
The distinction between ADS-B and TCAS is that the previous system is passive. It doesn’t actively interrogate plane as TCAS does. That’s why it will possibly’t give any Decision Advisories.
ADS-B offers extra exact, steady place updates, together with plane that TCAS may not interrogate at that second.
Nevertheless, normal TCAS II (even model 7.1) doesn’t at present use ADS-B inputs. Future variations of TCAS are more likely to make the most of ADS-B.
Future Applied sciences
ACAS X is a household of recent collision avoidance algorithms at present below improvement by the worldwide aviation sector. The “X” signifies it is a new method and isn’t simply an iteration of TCAS II. ACAS X makes use of superior computational strategies as a substitute of the prevailing TCAS’s rule-based logic.
ACAS X has completely different variants:
ACAS Xa: That is the direct successor to TCAS II for big transport plane. It is going to carry out the identical position however with fashionable laptop expertise. ACAS Xa is meant to be a plug-in substitute ultimately. It’ll use present transponder indicators however make smarter selections.
ACAS Xo: The “o” stands for “particular Operations” or “Optionally available use circumstances.” This variant is aimed toward situations that TCAS II doesn’t deal with properly. This contains intently spaced parallel approaches or operations like overtaking on oceanic routes. ACAS Xo would possibly enable horizontal RA directions in restricted conditions.
ACAS Xu: The “u” stands for Unmanned plane programs corresponding to drones. With massive drones and remotely piloted autos sharing airspace, there’s a necessity for collision avoidance designed particularly for them.
Drones gained’t have pilots to see-and-avoid, so ACAS Xu would function their collision avoidance mechanism. It might be built-in into drone autopilot logic to maneuver the drone away from conflicts routinely.
ACAS Xr: The “r” stands for Rotorcraft. Helicopters have completely different flight traits and infrequently function at decrease altitudes or slower speeds the place present TCAS isn’t used.
ACAS Xr will present collision avoidance designed for helicopters. This would possibly embrace completely different alerting thresholds since helicopters can flip or cease sooner but additionally usually fly low, the place TCAS-II could be inhibited. Incidents such because the 2025 Potomac river mid-air collision may probably be averted if helicopters use this expertise.
ACAS X programs are nonetheless in testing and validation phases as of 2025.
Conclusion
TCAS has essentially reworked flight security. Mid-air collisions in managed airspace are exceedingly uncommon today, particularly in comparison with aviation’s pre-TCAS period. Upcoming TCAS fashions corresponding to ACAS X promise to make flying even safer.
Even so, pilots should not depend on TCAS to bail them out of tight spots. Staying vigilant with seeing and avoiding, together with coordinating with ATC remains to be what retains plane safely aside.





